Why are vaccines so important?
Try to imagine a world that still suffers from smallpox or polio. Thanks to vaccines, among other things, such threats are history in most parts of the world today. But diseases like measles and COVID-19 help to underscore the fact that there is still a need for good immunization.
Vaccine trials are immunizations because they teach the body how to identify and protect itself from infection. But how are they developed? In scientific terms, what does it take to get to the efficacy, safety, and utility of a vaccine? It will therefore be helpful if we discuss the process in detail, so that understand the complexity of the incredible process above.
Step 1: Vaccine Research—The Foundation of Innovation
Each vaccine always begins with the proper vaccine research. This stage focuses on knowing the pathogen in the particular disease being studied which may be a virus, bacterium, or a parasite and even targets immunity.
Researchers ask critical questions during this phase:
- Which part of the pathogen should the immune system be aimed at?
- Is it possible to reduce virulence or to eliminate the pathogen for use in a vaccine?
- Is there anything that exists regarding other diseases similar to this?
Modern biotechnology tools like genomic sequencing have changed this step. For instance, with COVID-19 as the target point in the viral envelope, the spike protein was identified in weeks.

Step 2: In Vitro Analysis – From Cell Culture to Animals
It is after the emergence of a vaccine trials concept that it goes through preclinical testing. It ensures that the vaccine has no negative side effects and is efficient in areas that are artificially controlled.
Preclinical tests often include:
- In-vitro studies: Testing on cells in a lab.
- Animal models: In more complex species such as mice or monkeys monitoring immune responses.
Now how was animal immunization useful here? This is because animal studies generally indicate human reactions thereby minimizing risks in the later stages. Preclinical evaluation precedes the clinical evaluation involving the patient.
Step 3: Clinical Trials -The Savior of the Tests
Clinical trials are the final and most important and costly stage of the process of developing vaccines. They refer to the process where the vaccine is administered to human beings in various sessions with a view of ascertaining that is safe, effective and fit to be administered in the market.
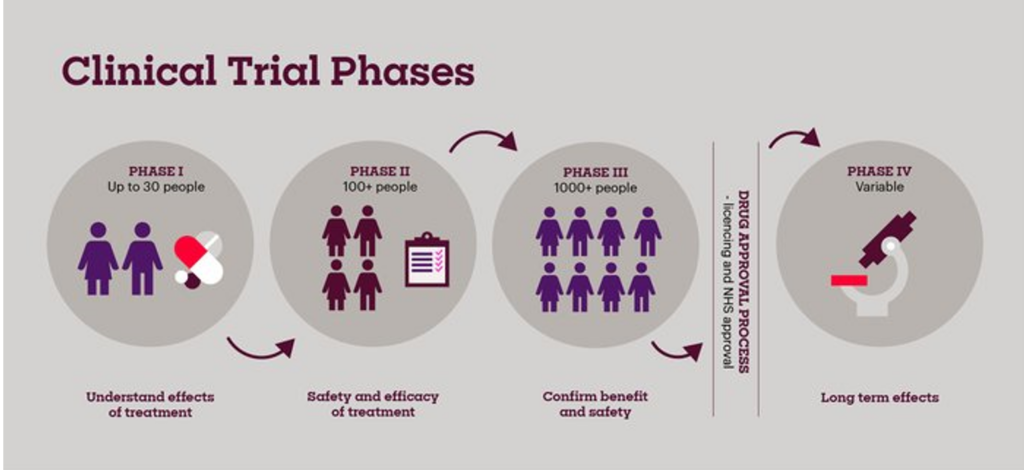
The Three Stages of Vaccine Testing are:
- Phase 1: Forums of a limited number of people are used to evaluate the effect of the vaccine.
- Phase 2: Several hundred volunteers assist in checking dosage and immune response details.
- Phase 3: Millions of people take part to ensure effectiveness and to determine adverse effects that occur very rarely.
Vaccine trials help decide which vaccines will or will not be approved. You probably did not know that only a paltry 10 % of all formulated vaccines ever reach the market.
Step 4: Regulatory Approval – The Last Stigma
Having tested its vaccine, a manufacturer presents the results to a regulatory agency such as the FDA in the United States, or EMA for the European market. Approval processes include:
- Data review in clinical trials.
- Checking the facilities used in vaccine manufacturing.
- Compliance with the safety standards as well as quality standards.
Some strict requisites need to be fulfilled for a vaccine that should be administered to society. Legitimate approval is a testimony that the vaccine is genuine and effective.

Step 5: Vaccine Manufacturing—From Theory to Practice
After that, the vaccine manufacturing goes through the process of large-scale production of vaccines, which is essential at this stage. Here’s how it works:
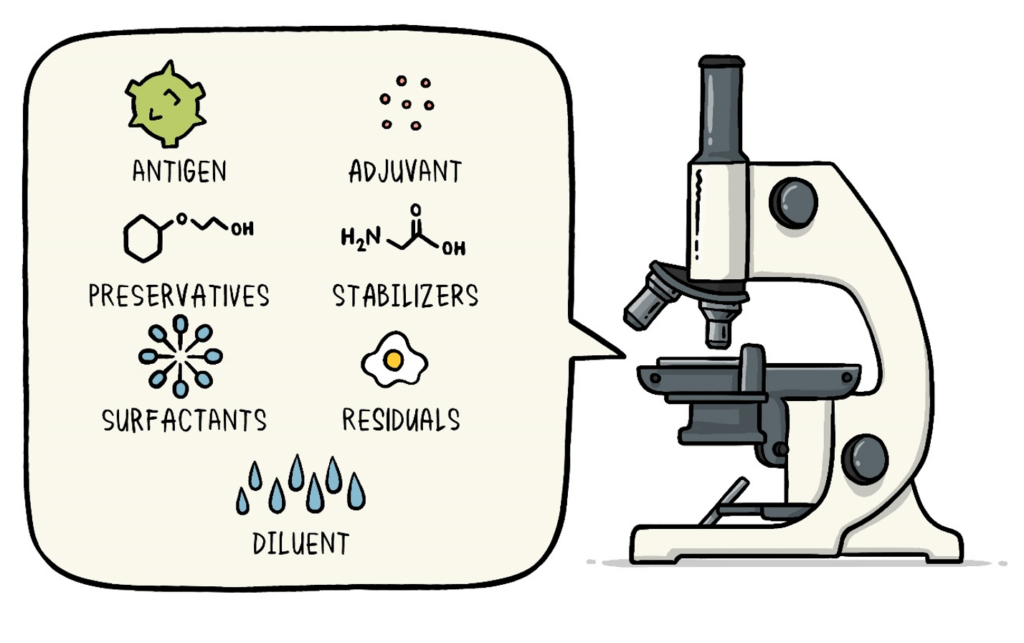
- Production of Antigens: The operational, or working, part of the vaccine is produced it may involve growing cells on a substrate or fermenting a culture.
- Purification: Some parts of the antigen are purged to ensure that the vaccine is safe for human use.
- Formulation: Some of the other ingredients include stabilizers and preservatives to increase the product’s shelf life.
Now the question is where does vaccine manufacturing occur? In a fully equipped production hall equipped to meet premium quality specifications. These amenities help to preserve the long-life gabion and free it from contaminants.
Fun Fact: mRNA technology has revolutionized the development process of vaccines, something exhibited through the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine against COVID-19.
Step 6: Distribution and Administration—Taking Vaccines to the Public
Mass production is by no means a surefire way to be successful on the market. Vaccine Manufacturing is only half the battle. In light of this, the vaccines must move around the world with the highest level of efficiency. This involves:
- Others were related to transportation and storage such as cold chain to ensure that the vaccines are stored at the right temperatures.
- This supports political involvement through Governments and Health Organizations.
- Implementation of free publicity for the vaccine.
Can you imagine some of the difficulties of delivering vaccines to hard-to-reach regions? Other examples of such inventions include portable coolers and mobile clinics, which are cutting across this gap.
Challenges in Vaccine Manufacturing
This is true because the initiatives to produce vaccines are not void of challenges. Key challenges include:
- High Costs: The challenges make the process a very expensive one since it involves a lot of vaccine research and vaccine trials.
- Rapid Mutations: It means that diseases such as the influenza virus necessitate continuous updates.
- Public Hesitancy: Such information can in effect hamper the drive towards immunization.
Nevertheless, biotechnology goes on advancing, guaranteeing people use vaccines as an integral part of their health.
Go visit our vaccine bioreactor (GMP) to get a quote.
Trends in Vaccine Development
The proactivity in biomolecular research applied to vaccines is very bright. Emerging trends include:
- mRNA Vaccines: Potential cure for a lot of diseases but the major one being covid 19.
- Personalized Vaccines: Based on their unique genetic information.
- Global Collaboration: Completing the development with the help of knowledge.
Think how amazing it would be if vaccine manufacturing occurred in a few weeks instead of years. The two technologies, biotechnology, and artificial intelligence, have made this vision possible.
Conclusion
Vaccines are one of the greatest examples of innovation and determination that man has come through. As for basic vaccine discovery, various processes of conducting vaccine trials, as well as vaccine manufacturing, all aim to provide safer products that are useful for saving lives.
If you are interested in knowing how biotechnology influences our lives, just stay tuned! Do visit BaiLun Bio and explore the realm of vaccines and much more. Combined, we can get informed, get creative, and grow.
FAQs
Q1: What are vaccine trials?
Vaccine trials are clinical studies of the efficiency, safety and dosage of the vaccine before they are made available to the public.
Q2: How does vaccine manufacturing conform to quality?
From, the main quality control measures employed during the fabrication of antigens, purification, as well as formulation of the vaccine to achieve safety and efficacy.
Q3: Why has the search for vaccines been deemed relevant?
It finds out the targets of disease and creates means of counteracting pathogens, forming the basis of safe immunization.
