Unlocking the Science: The Biosynthesis of Carbohydrates and Its Role in Metabolism
Biosynthesis of carbohydrates is one of the basic metabolic activities in all living forms since they act as energy storage materials that are important to life. Carbohydrates are the major energy supplying molecules in the cells, and the formation of carbohydrates is a vital cellular function which exists so that life can continue. It exists in the form of simple sugars to complex polysaccharides wherein this metabolic pathways carbphydrates powers cellular processes, gives strength to structures, and maintains metabolic balance.
Reconaissance on carbohydrate synthesis is significant in explaining the conversion of energy resources to forms useful to the organisms in a given environment. These are controlled by metabolic pathways carbohydrates go through to maintain the energy balance and cellular function. In the following article, the reader will learn the process of biosynthesis of carbohydrates, its relevance, and the biochemical reactions regarding it.
The Fundamentals of Biosynthesis of Carbohydrates
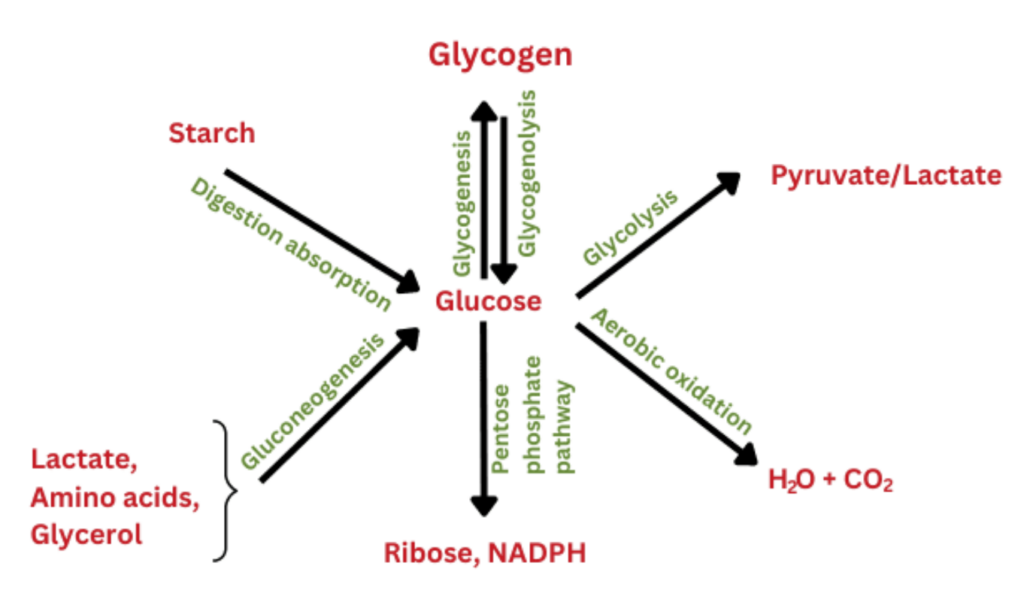
Carbohydrate synthesis is a process through which living organisms build carbohydrates from small molecules that are organic in nature. This occurs in plants, animals and microorganisms with the aim of providing the cell with glucose and other sugars that are required for different activities.
Glycogenesis is one of the several metabolic processes that carbohydrates undergo, others being gluconeogenesis, and photosynthesis. These processes build up more complex sugars and polysaccharides from raw materials like carbon dioxide, pyruvate and other molecules produced during the citric acid cycle.

Key Functions of Carbohydrate Synthesis
Here are some key functions of carbohydrates synthesis:
- Ensures that glucose is always available to the body for the provision of energy in the process of energy metabolism.
- Supports structural components in plants and microorganisms (e.g., cellulose, chitin).
- Acts as a precursor for nucleotides, glycoproteins, and glycolipids.
- Stores energy in the form of glycogen in animals and starch in plants.
Photosynthesis: The Primary Carbohydrate Synthesis Pathway
It is a widely known fact that the biosynthesis of carbohydrates takes place in plants and cyanobacteria through the process of photosynthesis. This process plays an important role of converting light energy to chemical energy so as to synthesize glucose and other sugars.
Steps of Photosynthetic Carbohydrate Synthesis
Light-Dependent Reactions:
- They are situated at the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts.
- To do this, solar energy is converted to ATP and NADPH which are used in performing the following roles.
Calvin Cycle (Light-Independent Reactions):
- Occurs at the chloroplasts stroma the organelle found in plant cells or in the cytoplasm of some algae.
- Carbamoyl phosphate and NADPH are used to fix carbon dioxide into glucose.
The Calvin cycle is the most important pathway of carbon fixation in plants and it is responsible for biosynthesis of carbohydrates, formation of glucose and its further conversion into starch and cellulose.
Gluconeogenesis: Biosynthesis of Carbohydrates in Animals and Humans
While plants use photosynthesis for the carbohydrates synthesis, animals and human beings use gluconeogenesis when dietary glucose cannot be obtained. It occurs predominantly in the liver and, to a smaller measure, in the kidneys.
Key Steps in Gluconeogenesis:
Conversion of Pyruvate to Oxaloacetate:
- Pyruvate that was produced from amino acids and lactate is transformed into oxaloacetate by the help of the enzyme called pyruvate carboxylase.
Formation of Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP):
- PEP is formed from oxaloacetate through the action of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase.
Synthesis of Fructose-6-Phosphate:
In the series of reactions, PEP is then converted into fructose-6-phosphate.
Glucose Formation:
Lastly, fructose-6-phosphate is converted into glucose-6-phosphate and the latter can be released into the circulation or stored as glycogen.
Gluconeogenesis is one of the metabolic pathways carbohydrates go through to ensure a constant supply of glucose in the body especially when fasting, during exercises or periods of metabolic stress.
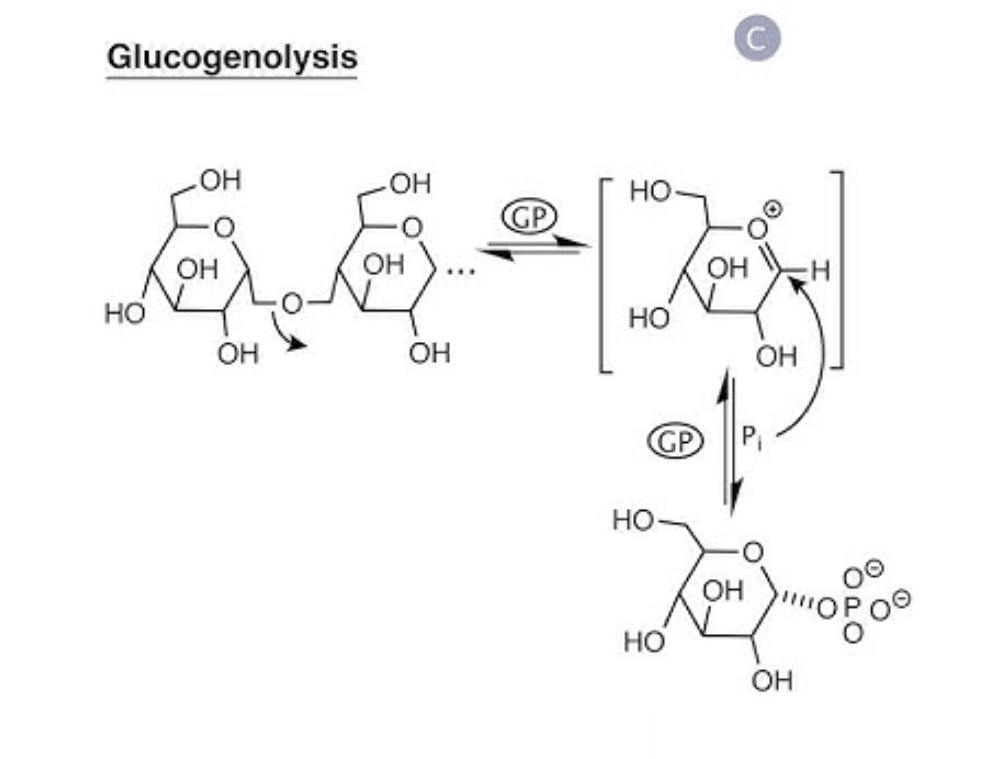
Glycogenesis and Glycogenolysis: Storing and Releasing Energy
Glycogenesis is a process through which glucose is preserved in the human body in the form of glycogen. In glycogenolysis, glycogen is also utilized as a source of glucose when necessary.
Glycogenesis (Storage of Carbohydrates)
- Glycogen is formed by the joining of glucose molecules with the help of glycogen synthase enzyme.
- Activated by the glycogen synthase enzyme.
- It involves the liver and skeletal muscles most of the time.
Glycogenolysis (Release of Stored Glucose)
- Glycogen is broken down into glucose-1-phosphate.
- Converted into glucose-6-phosphate for energy production.
- It is stimulated during fasting, exercise, and stressful conditions.
Glycogenesis and glycogenolysis are two metabolic pathways carbohydrates that act on carbohydrates in cars to ensure that there is an adequate supply of glucose in the bloodstream and to provide energy when required.
Role of the Pentose Phosphate Pathway in Carbohydrate Synthesis
The other pathway of the biosynthesis of carbohydrates is the pentose phosphate pathway which plays another important role in the provision of molecules to the cells.
Functions of the Pentose Phosphate Pathway:
- Generates ribose-5-phosphate for nucleotide synthesis.
- Produces NADPH for anabolic reactions and antioxidant defense.
- Supports fatty acid and cholesterol biosynthesis.
This is another pathway and occurs alongside glycolysis to ensure the cells are healthy and in appropriate energy balance.
Disorders Related to Biosynthesis of Carbohydrates
The problems in the carbohydrate synthesis pathways cause metabolic disorder which include:
- Diabetes Mellitus: Impaired glucose metabolism due to insulin deficiency or resistance.
- Glycogen Storage Diseases: These are inherited biochemical disorders affecting glycogen metabolism.
- Galactosemia: Poor ability to metabolize galactose and is toxic to the body.
Studying these disorders reveals that carbohydrates have a crucial role in the production of carbohydrates in the body.
Advances in Research on Carbohydrate Synthesis
Publication in the field of biosynthesis of carbohydrates and pharmaceutical and biotechnological applications have been discovered in the recent past. Some key developments include:
- Synthetic Biology Techniques: Microbial engineering for synthesis of highly branched carbohydrates.
- From the research done, it is evident that CRISPR gene editing can be used to modify the metabolic pathways carbohydrates to increase the synthesis of carbohydrates.
- Pharmacogenomics in diabetes and metabolic disease: metabolomic approach to drug development.
These advances pave the way to better development of therapies, to be useful in industries and also to advance the knowledge in metabolic health.
Conclusion
Carbohydrate synthesis is crucial for multiple metabolic processes and structural development in all of the life forms, which is why it plays a significant role in metabolic biology. From the process of carbon fixation in plants to the process of gluconeogenesis in the body of a human, carbohydrate synthesis and its mechanisms guarantee a steady need of energy and biomolecules. Exploring the numerous pathways through which carbohydrates metabolism is conducted helps in effective treatment of patients suffering from metabolic disorders and to enhance health through right diets.
There are many potential developments that biosynthesis of carbohydrates will uncover in the future of the biotechnology, medicine, and food Industries. Carbohydrates in the natural environment or in laboratory solutions and experiments become essential elements of life because of the synthesis and regulation skills.
