Being a detailed process, you must consider different measures for scale-up success. In this elaborative guide, we shall be taking a look at everything you should know about the process. We’ll delve into what scaling involves, different kinds of scale-ups, and scaling factors to keep in mind.
What Does a Scale Up Involve?
Bioreactor scale up is the process of increasing working fermentation volumes from small-scale fermentation to large-scale fermentation.
Small-scale fermentation is essential in studies and testing. However, after all the parameters or variables have been studied, you have to migrate to larger-scale fermentation. It is at this point that scaling up occurs.
Scale-up can be complex, expensive, and time-consuming. But if done correctly, the outcome is an effective, long-running duplicate from the small-scale version. Here are steps to follow.
1. Preparation
Properly curated planning and preparation for bioreactor scale-up directly determines the success of your bioprocess. It is at this stage that you decide between different bioreactor scale-up parameters and determine various factors including:
- Expected Outcomes: Clearly identify the demand for your product and what level of production you are trying to achieve at a larger scale. Having realistic end goals will let you know when and where to start your scale-up.
- Working mode: Before upscaling, it is important to know how long and how often the reactor will be in use. This will guide you on the method of scale up and type of bioreactor you need to increase your production. For instance, if you prefer single-use bioreactors, scale up according to cleaning times.
- Perform fermentation data analytics: this will give you an idea of how much loss you incur while purifying the product at a larger scale compared to a smaller scale.
2. Consultation
Scaling up a bioreactor must involve experienced and skilled hands as this is a rather complicated and sensitive process. If you don’t have the know-how of how to navigate through the scale up, reach out to experts in the field. Find certified engineers and other technicians who have already handled the scale up needed.
3. Testing
Before scaling up your bioreactor, test various parameters using a bench scale bioreactor.
A bench scale is the smallest footprint bioreactor with an appropriate size for fundamental research and testing. Therefore, combining a bench scale’s capabilities with more complex methods for large-scale production will help you achieve a successful scale-up.
This is why the small and inexpensive bench-scale bioreactors are very useful in predicting how effective the large-scale bioreactor will be in respect to these parameters.
4. Scaling up
After due diligence, it is now time for the actual procedure. But before that, you have to take various factors into account. Moreover, there are various ways to do a bioreactor scale-up — which we are going to discuss.
5. Assess results
The beginning of this next step involves comparing current results with initial production at the end of your scale-up procedure to determine whether the whole process is successful. Therefore, to evaluate this, you have to calculate the ratio from the smaller-scale phase to the large-scale phase with the help of a bioreactor scale up calculator.
This is not a one-time activity but an ongoing process you should perform to validate if your scale up is consistently successful.
Bioreactor Scale up Methods
There are three main methods to scale your bioreactor. Each method is different, and you can choose which best suits production needs. Here is a comprehensive layout of each method.
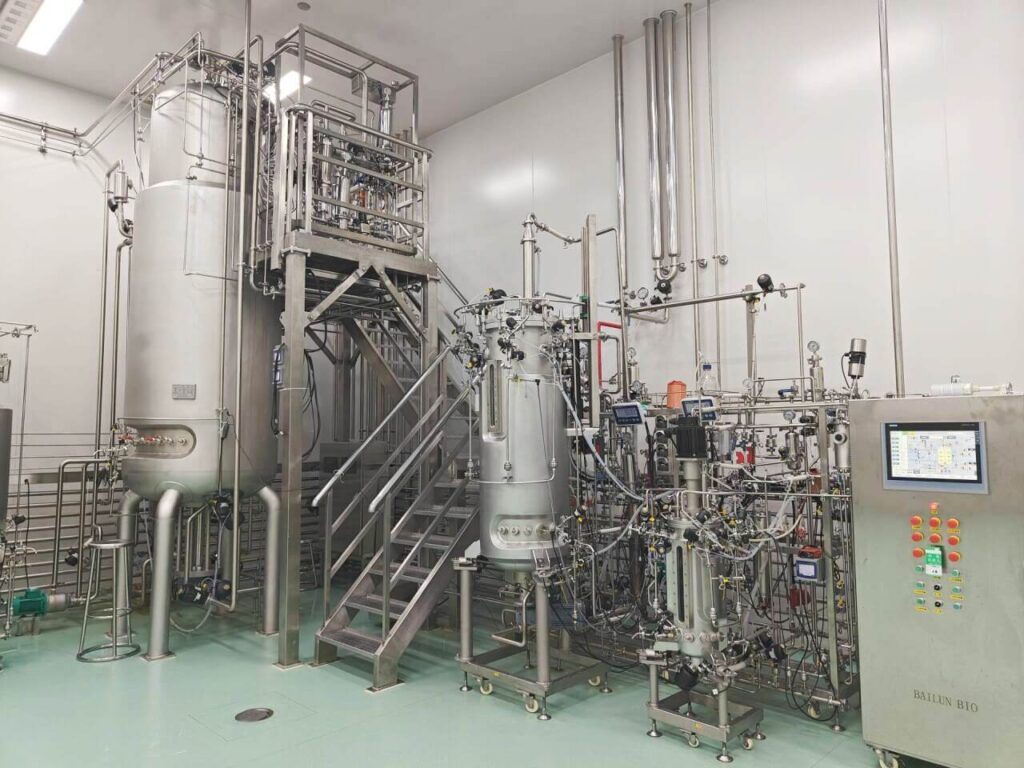

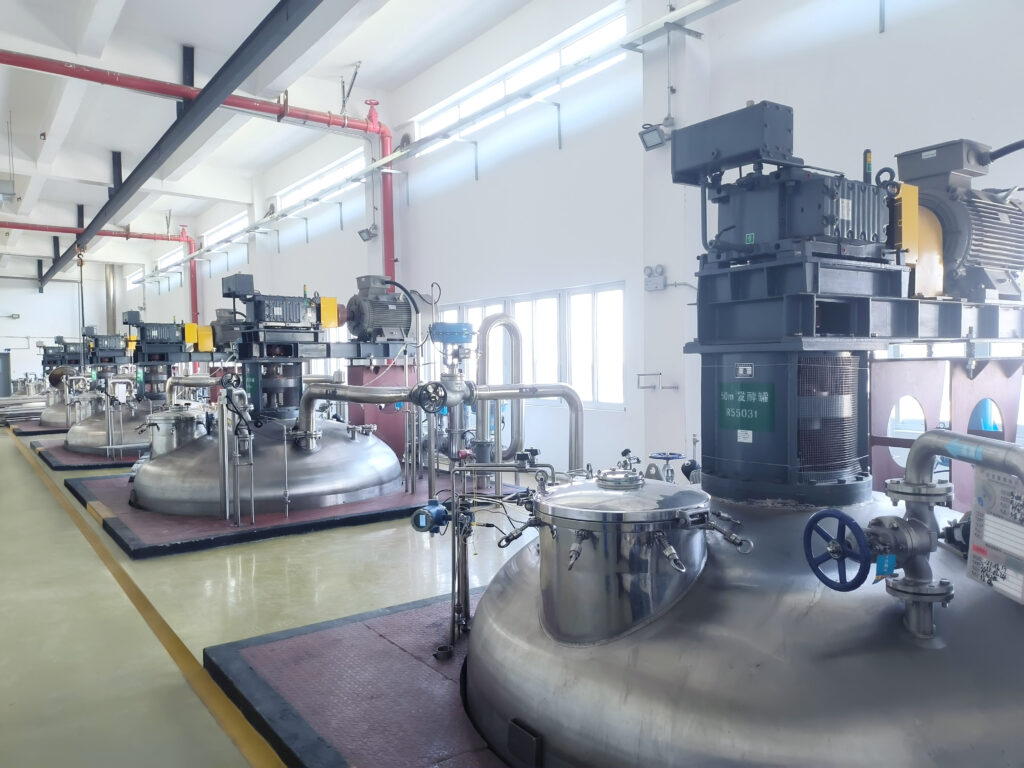
1. Scaling up by volume
Scaling up by volume simply involves increasing the rate of production on a fixed ratio. It entails increasing the power and size of the already existing bioreactor.
Stirred tank bioreactors are the most common variety to scale up. This is because they meet the industry requirements due to the ability to effectively mix fluid and facilitate oxygen transfer.
There are three scales to choose from, depending on the production levels you want to realize. They are:
- Laboratory scale: Volumes range from 0.5 to 10 L. This scale is usually applied to small-scale productions and test purposes. They are helpful if you want to test the behavior of cell cultures.
- Pilot scale – Pilot scale bioreactorsrange between 50l and 200l. They are mainly used for small-scale operations or testing to kickstart product development before increasing production to a larger scale.
- Industrial scale – Between 500l and 5000l after scale-up for large-scale production. It is the commercialization stage, allowing you to produce larger quantities.
Advantages of scaling up by volume
- The conditions remain constant and that all cells grow in the same environment, producing identical results.
- There is room to scale up to the desired product quantity.
Disadvantages of scaling up by volume
- Scaling up by volume is challenging. This is because there are many factors that you have to consider and keep constant as you increase production.
- This method is time consuming because it involves numerous factors that must be taken into account for balanced results.
- There is always the major risk of failure even after carefully studying the conditions in one scale and applying them to a different scale.
- It can be expensive, especially when the whole batch has to be discarded when even the tiniest contamination occurs.
2. Scaling up by unit
Contrary to the concept of scaling up a bioreactor by increasing the capacity of existing equipment,scaling up by unit involves increasing the number of bioreactors. This means that each bioreactor has a small volume, and their capacities add up to the desired production scale.
Some of the resources that you can use to perform this method are;
- Roller bottles – The medium is added at the bottom and the adherent cells attach to the walls as the bottle rolls. This means that the cells get a constant supply of medium on a larger scale. This is why roller bottles were previously used for vaccine production.

Roller bottles for bioreactor scale up - T-flasks – They have vented filter caps which allow gas exchange to take place. You can also fill them with any volume and use them to grow cells for various purposes.
Advantages
- To increase production, you simply add more roller bottles or T-flasks until you achieve your desired outcome.
- You don’t need to go through the process of purchasing a new bioreactor and it is proven to produce reliable results.
- Scaling out is less costly, In case of contamination, you can remove or replace the contaminated flask or bottle without incurring much costs.
Disadvantages
- The more resources you add to increase the production scale, the more space and labor you require.
- Bottles and flasks may vary in performance, so the quality of outcomes can deviate.
3. Single use bioreactors
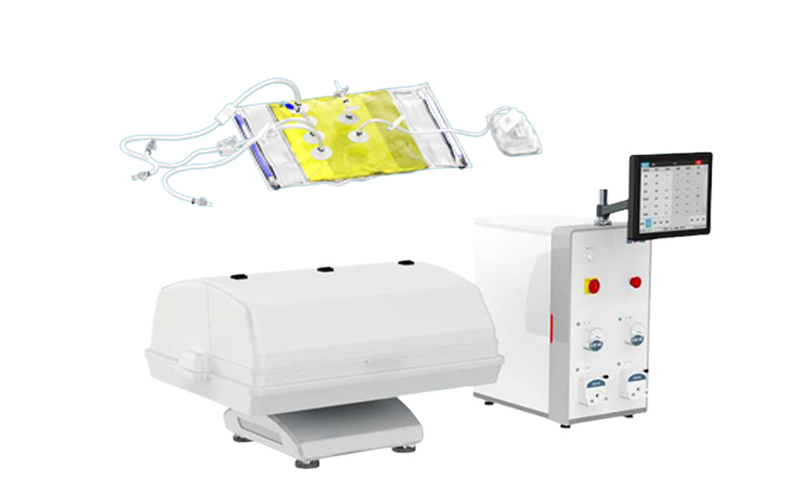

With technological advancements in the bioprocessing industry, one of the most exciting innovations has been the single use bioreactor. Instead of a glass or stainless steel, a single use bioreactor comprises a disposable bag in a permanent structure such as a cylinder.
These types of bioreactors are used to grow cells on a large-scale basis for various processes. But they also come in handy during a bioreactor scale up.
Instead of getting a new bioreactor or adding more resources to an existing one, you can use a single use bioreactor to increase your production scale while keeping all conditions constant.
Advantages
- A single use bioreactor saves time. You just have to install it separately without affecting the operations of your current bioreactor.
- The disposable bags offer the convenience of saving you the labor and time you would use to clean a regular bioreactor.
- You don’t have to incur any validation costs once you test and approve that thesingle use bioreactors are suitable for your production type and scale.
Disadvantages
- Scale up is limited to just 2000l. Any higher volume is likely to overstretch and cause the bag to burst.
- Single use bioreactors are expensive, especially if you require the best quality of plastic bag. Choosing cheaper, substandard ones could cause the plastic to leach into your products and affect quality.
Factors to Consider When Scaling Up a Bioreactor
Scaling up a bioreactor is a complex process with many factors to consider. These conditions may directly or indirectly affect the efficiency of your scale up and the overall production quality. They include;
1. kLa
kLa is simply a measure of how gasses transform into liquids. The essence of this parameter is helping you define the limits of your bioprocess. It is influenced by the types and amount of gasses in the bioreactor system, in that a high kLa means that your system is able to transfer oxygen efficiently.
2. Mixing time
You also have to consider the period it takes to achieve uniformity in the liquid. This is referred to as mixing time
Mixing time is directly influenced by the type of bioreactor and the rate of stirring. It is a crucial factor that will help you determine if you have to change your bioreactor’s configuration as you scale up.
3. Scale
Before a scale up, you must understand the capacity of your bioreactor and how high you want to get your production rate. This will help you achieve a balance for all operating conditions and ensure that the bioreactor scale up will not affect your product quality.
4. Physical factors
A scale up involves increasing production size, which may lead to less space for some processes and reactions. Therefore, you have to ensure that you leave enough design space for formulation of gasses, foam and bubble formation, and efficient mixing.
Other physical factors that affect a bioreactor scale up include equipment geometry, aeration, and heat transfer. These are all crucial parameters to keep in mind for an effective scale up.
5. Gas transfer
Gas transfer refers to the rate at which gasses are delivered to the bioreactor according to the pressure and mode of injection. It is also an important parameter as it directly affects foam formation and cell concentration in various production scales.

How to Increase the Efficiency of Your Scale Up
The results of your bioreactor scale up directly affect the quantity and quality of your processes. Therefore, here are some ways to increase the efficiency of the scale up for the best possible outcomes.
- Leverage data: Data is crucial for any bioprocess,more so in fermentation. To use data analytics for a bioreactor scale up, you need to identify trends and patterns across different scales during the scale up process to forecast performance. Moreover, using a bioreactor scale-up calculator will save you a lot of effort and money as opposed to doing things manually.
- Maintain a constant environment: When gradually increasing production scales, keep the cellular environment consistent so that you can effectively compare product quality and metabolic processes.
- Monitor scaling closely: For the best results, monitor and control key conditions and parameters such as temperature, pH, and oxygen levels regularly.
- Choose the right method: The three main methods of scaling up your bioreactor vary in efficiency according to your type of bioreactor, scale, and expected outcomes. Choose between them wisely.
- Test extensively – Before moving forward on any expansion or modification, carry out real-world experiments or virtual simulations to avoid incurring costs on untested processes.
Conclusion
When undertaking such an arduous process as a bioreactor scale up, it’s crucial to perform research and plan ahead. This entails understanding bioreactors and how they work, assessing possible risks, and taking into account various factors.
You must also understand different scale up criteria for bioreactors and set realistic expectations and take every possible measure to get the best out of your scale up.
One of the measures is partnering with the best professionals in the industry. At Bailun technologies, we offer the best solutions for your bioprocessing needs.
Are you ready to scale up your bioreactor to the next level? If so, contact us today and talk to our seasoned team of experts.


